Disaster Management Aspects
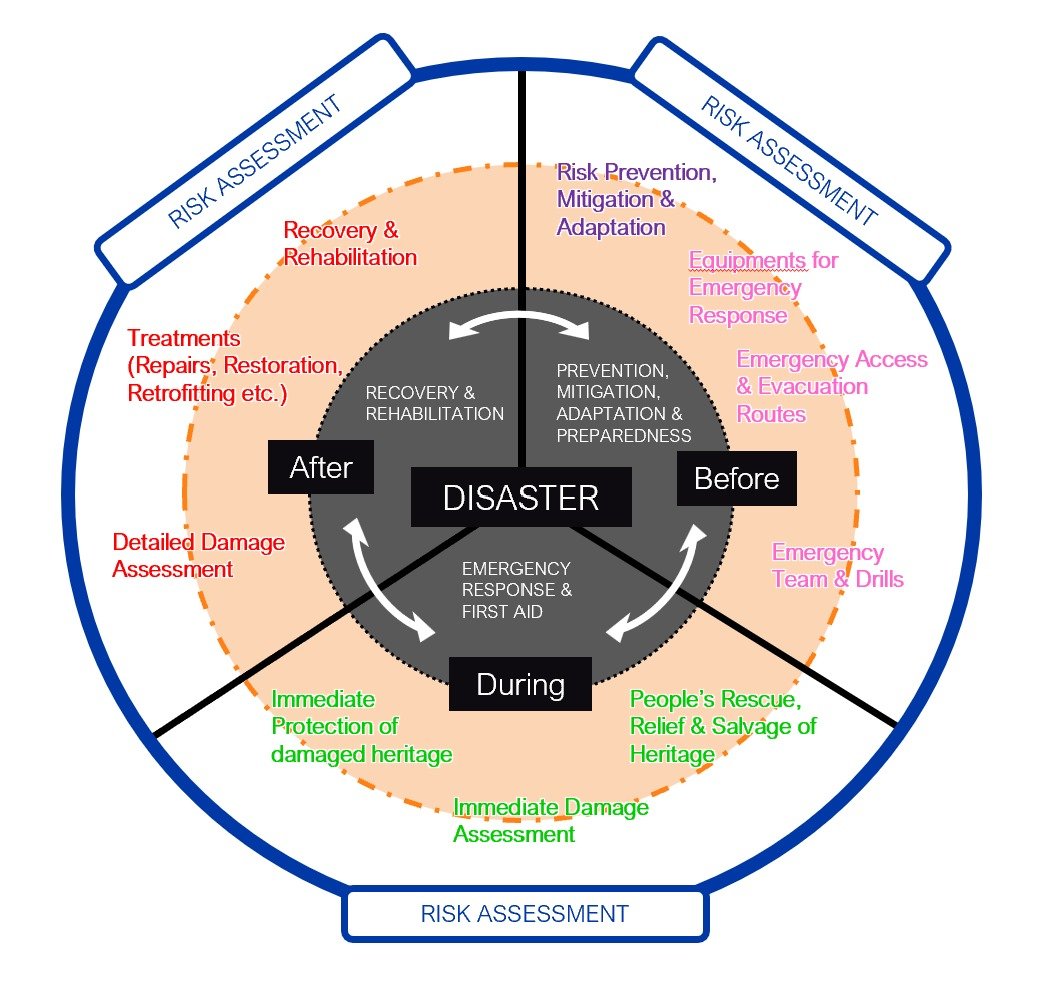
DRM Cycle for Cultural Heritage
C: R-DMUCH
Authors: Rohit Jigyasu & Dowon Kim

Preparedness
is the knowledge and capacity developed by communities and individuals to effectively anticipate, respond to and recover from the impacts of likely, imminent or current disasters. It is based on a sound analysis of disaster risks and good linkages with early warning systems, and includes such activities as contingency planning, the stockpiling of equipment and supplies, the development of arrangements for coordination, evacuation and public information, and associated training and field exercises.
Mitigation
is the lessening or minimizing of the adverse impacts of a hazardous event. Mitigation measures include engineering techniques and hazard-resistant construction as well as improved environmental and social policies and public awareness. In climate change policy, mitigation refers to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions that are the source of climate change.


Response
is the actions taken directly before, during or immediately after a disaster in order to save lives, reduce health impacts, ensure public safety and meet the basic subsistence needs of the people affected. Response is predominantly focused on immediate and short-term needs and is sometimes called disaster relief. Response relies on disaster risk-informed preparedness measures, such as contingency planning, early warning systems, emergency services and public assistance.
Recovery
is the restoring or improving of livelihoods and health, as well as economic, physical, social, cultural, and environmental assets, systems and activities, of a disaster-affected community or society, aligning with the principles of sustainable development and “build back better”, to avoid or reduce future disaster risk.


Adaptation
is the adjustment in natural or human systems in response to actual or expected climatic stimuli or their effects, which moderates harm or exploits beneficial opportunities. Adaptation is one of the key strategies to reduce disaster risk and enhance resilience to climate change impacts.
Hazard Monitoring
is the continuous or periodic observation and measurement of hazardous phenomena to provide information for analysis and early warning. Hazard monitoring is an essential component of an early warning system, which is an integrated system of hazard monitoring, forecasting and prediction, disaster risk assessment, communication and preparedness activities, systems and processes that enables individuals, communities, governments, businesses, and others to take timely action to reduce disaster risks in advance of hazardous events.
References
UNDRR. (2017). Disaster Risk Reduction Terminology. Retrieved from The Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) Glossary: https://www.undrr.org/drr-glossary/terminology
UNDRR. (2022). Words into Action: Using Traditional and Indigenous Knowledges for Disaster Risk Reduction. Retrieved from UNDRR: https://www.undrr.org/words-action-using-traditional-and-indigenous-knowledges-disaster-risk-reduction
